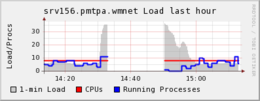
График системы
Ganglia, отображающий количество правок статей в Википедии. Отчетливо виден интервал когда сервер
Викимедиа перестал отвечать.
Ganglia (МФА: ˊgæŋglɪə) — масштабируемая распределенная система мониторинга кластеров[1] параллельных и распределенных (англ. grid) вычислений и облачных систем с иерархической структурой. Позволяет наблюдать статистику и историю (загруженность процессоров, сети) вычислений в реальном времени для каждой из наблюдаемых машин.[2][3]
Проект Ganglia был создан в 1998 году в Калифорнийском университете в Беркли как продолжение проекта Millennium, который был инициирован Национальным научным фондом США.[2][4]
Назначение и применение
Система построена по иерархическому принципу для интеграции кластеров. Для мониторинга состояния кластеров и их объединения используется древовидная система основанная на P2P соединениях и широковещательных протоколах. Система использует широко известные технологии: XML для представления данных, XDR для сжатия данных, RRDtool для хранения и визуализации данных. Она построена на базе тщательно спроектированных алгоритмов и структур данных, что обеспечивает надёжность, позволяет свести к минимуму накладные расходы на каждом из узлов и достичь высокой степени параллелизма. Для отображения страниц статистики используется шаблонизатор TemplatePower.[5]
Система была портирована на широкий спектр операционных систем и процессорных архитектур, и в настоящее время используется на более чем 500 кластеров по всему миру. Существует возможность установки Ganglia на следующие операционные системы: Linux (i386, ia64, sparc, alpha, powerpc, m68k, mips, arm, hppa, s390), FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonflyBSD, MacOS X, Solaris, AIX, IRIX, Tru64, HPUX и Windows NT/XP/2000/2003/2008.[6] Ganglia используется для связи кластеров в университетских кампусах по всему миру и может масштабироваться для обработки кластеров имеющих до 2000 узлов в своем составе.
Установка
Необходимые пакеты для установки системы Ganglia присутствуют в большинстве современных репозиториев операционных систем, построенных на базе ОС GNU Linux. Поэтому процесс установки не представляет особых сложностей. В Ubuntu необходимо выполнить команду:
sudo apt-get install ganglia-monitor ganglia-webfrontend chkconfig
Мы устанавливаем программу chkconfig для того чтобы иметь возможность управлять автоматическим запуском демонов при старте системы. В Fedora chkconfig как правило уже есть в системе, поэтому команда установки сокращается до:
sudo yum install ganglia
sudo yum install ganglia-gmond
Предполагается, что веб-сервер уже установлен. После установки вы можете открыть страницу статистики Ganglia, для это перейдите по адресу:
http://localhost/ganglia/
Если открыть страницу не удалось, то необходимо скопировать конфигурационный файл пакета ganglia-webfrontend в папку конфигурации виртуальных хостов Apache:
cp /etc/ganglia-webfrontend/apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf.d/ganglia-webfrontend.conf
service apache2 restart
Демоны gmetad и gmond должны запускаться автоматически при старте системы, для того чтобы проверить так ли это необходимо выполнить команду:
chkconfig --list|grep '^gm[etaon]*d'
gmetad 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
gmond 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
В результате выполнения команды мы должны увидеть gmetad и/илиgmond с опциями загрузки «on». Если на всех уровнях выставлено значение «off», то можно включить сервисы командой:
chkconfig --level 2345 gmetad on
chkconfig --level 2345 gmond on
это сработает только в том случае, если демоны зарегистрированы как сервисы. Если нет, то можно прописать старт демона вручную, скопировав скрипт запуска из директории с исходным кодом Ganglia в директорию инициализации системы:[6]
% cp ./gmond/gmond.init /etc/rc.d/init.d/gmond
% chkconfig --add gmond
% chkconfig --list gmond
gmond 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
% /etc/rc.d/init.d/gmond start
Starting GANGLIA gmond: [ OK ]
Однако в Ubuntu вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, потому что в этой ОС используется отличная от других систем структура директорий инициализации системы. Поэтому иногда может понадобится создать несколько символических ссылок, для подмены несуществующих директорий, которые использует Ganglia:[7]
mkdir /etc/rc.d
mkdir /etc/rc.d/init.d
ln -s /lib/lsb/init-functions /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
Настройка
Имя кластера прописывается в файле /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf. Если необходимо назначить кластеру имя clustername, то нужно прописать:
cluster {
name = "clustername"
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
В качестве IP адреса по умолчанию используется 239.2.11.71, его можно прописывать как дополнительный для интерфейса который соединен с кластером.
route add -host 239.2.11.71 dev eth1
Источники данных указываются в конфигурационном файле демона gmetad — gmetad.conf:
data_source "Кластер 1" 127.0.0.1 1.2.3.4:8655 1.2.3.5:8625
data_source "Кластер 2" 1.2.4.4:8655
Для того чтобы увидеть в каком виде Ganglia получает данные с хостов необходимо выполнить в терминале команду:
telnet localhost 8649
полный вывод команды (англ.)
root@host:/etc# telnet localhost 8649
Trying ::1...
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" standalone="yes"?>
<!DOCTYPE GANGLIA_XML [
<!ELEMENT GANGLIA_XML (GRID|CLUSTER|HOST)*>
<!ATTLIST GANGLIA_XML VERSION CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST GANGLIA_XML SOURCE CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT GRID (CLUSTER | GRID | HOSTS | METRICS)*>
<!ATTLIST GRID NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST GRID AUTHORITY CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST GRID LOCALTIME CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ELEMENT CLUSTER (HOST | HOSTS | METRICS)*>
<!ATTLIST CLUSTER NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST CLUSTER OWNER CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST CLUSTER LATLONG CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST CLUSTER URL CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST CLUSTER LOCALTIME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT HOST (METRIC)*>
<!ATTLIST HOST NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST HOST IP CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST HOST LOCATION CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST HOST REPORTED CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST HOST TN CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST HOST TMAX CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST HOST DMAX CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST HOST GMOND_STARTED CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ELEMENT METRIC (EXTRA_DATA*)>
<!ATTLIST METRIC NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC VAL CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC TYPE (string | int8 | uint8 | int16 | uint16 | int32 | uint32 | float | double | timestamp) #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC UNITS CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC TN CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC TMAX CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC DMAX CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC SLOPE (zero | positive | negative | both | unspecified) #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRIC SOURCE (gmond) 'gmond'>
<!ELEMENT EXTRA_DATA (EXTRA_ELEMENT*)>
<!ELEMENT EXTRA_ELEMENT EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST EXTRA_ELEMENT VAL CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT HOSTS EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST HOSTS UP CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST HOSTS DOWN CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST HOSTS SOURCE (gmond | gmetad) #REQUIRED>
<!ELEMENT METRICS (EXTRA_DATA*)>
<!ATTLIST METRICS NAME CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS SUM CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS NUM CDATA #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS TYPE (string | int8 | uint8 | int16 | uint16 | int32 | uint32 | float | double | timestamp) #REQUIRED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS UNITS CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS SLOPE (zero | positive | negative | both | unspecified) #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST METRICS SOURCE (gmond) 'gmond'>
]>
<GANGLIA_XML VERSION="3.1.7" SOURCE="gmond">
<CLUSTER NAME="unspecified" LOCALTIME="1293106689" OWNER="unspecified" LATLONG="unspecified" URL="unspecified">
<HOST NAME="old" IP="30.30.30.2" REPORTED="1293106678" TN="11" TMAX="20" DMAX="0" LOCATION="unspecified" GMOND_STARTED="1293092118">
<METRIC NAME="load_one" VAL="1.33" TYPE="float" UNITS=" " TN="70" TMAX="70" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="load"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="One minute load average"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="One Minute Load Average"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="mem_total" VAL="895772" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total amount of memory displayed in KBs"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Memory Total"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="os_release" VAL="2.6.35-24-generic" TYPE="string" UNITS="" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="system"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Operating system release date"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Operating System Release"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="proc_run" VAL="0" TYPE="uint32" UNITS=" " TN="0" TMAX="950" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="process"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total number of running processes"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Total Running Processes"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="load_five" VAL="1.08" TYPE="float" UNITS=" " TN="70" TMAX="325" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="load"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Five minute load average"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Five Minute Load Average"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="gexec" VAL="OFF" TYPE="string" UNITS="" TN="160" TMAX="300" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="core"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="gexec available"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Gexec Status"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="disk_free" VAL="13.353" TYPE="double" UNITS="GB" TN="20" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="disk"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total free disk space"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Disk Space Available"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="mem_cached" VAL="211464" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="0" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Amount of cached memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Cached Memory"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="pkts_in" VAL="2.40" TYPE="float" UNITS="packets/sec" TN="0" TMAX="300" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="network"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Packets in per second"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Packets Received"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="bytes_in" VAL="2405.43" TYPE="float" UNITS="bytes/sec" TN="0" TMAX="300" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="network"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Number of bytes in per second"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Bytes Received"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="bytes_out" VAL="322.05" TYPE="float" UNITS="bytes/sec" TN="0" TMAX="300" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="network"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Number of bytes out per second"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Bytes Sent"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="swap_total" VAL="0" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total amount of swap space displayed in KBs"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Swap Space Total"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="mem_free" VAL="92964" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="0" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Amount of available memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Free Memory"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="load_fifteen" VAL="1.02" TYPE="float" UNITS=" " TN="70" TMAX="950" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="load"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Fifteen minute load average"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Fifteen Minute Load Average"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="os_name" VAL="Linux" TYPE="string" UNITS="" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="system"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Operating system name"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Operating System"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="boottime" VAL="1293091899" TYPE="uint32" UNITS="s" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="system"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="The last time that the system was started"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Last Boot Time"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_idle" VAL="89.1" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="90" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle and the system did not have an outstanding disk I/O request"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU Idle"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_user" VAL="7.9" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="90" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU User"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_nice" VAL="0.1" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="90" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level with nice priority"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU Nice"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_aidle" VAL="68.9" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="3800" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percent of time since boot idle CPU"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU aidle"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="mem_buffers" VAL="31112" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="0" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Amount of buffered memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Memory Buffers"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_system" VAL="1.3" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="90" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the system level"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU System"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="part_max_used" VAL="78.0" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="20" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="disk"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Maximum percent used for all partitions"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Maximum Disk Space Used"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="disk_total" VAL="39.429" TYPE="double" UNITS="GB" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="disk"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total available disk space"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Total Disk Space"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="mem_shared" VAL="0" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="0" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Amount of shared memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Shared Memory"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_wio" VAL="1.5" TYPE="float" UNITS="%" TN="0" TMAX="90" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle during which the system had an outstanding disk I/O request"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU wio"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="machine_type" VAL="x86" TYPE="string" UNITS="" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="system"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="System architecture"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Machine Type"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="proc_total" VAL="368" TYPE="uint32" UNITS=" " TN="0" TMAX="950" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="process"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total number of processes"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Total Processes"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_num" VAL="1" TYPE="uint16" UNITS="CPUs" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Total number of CPUs"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU Count"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="cpu_speed" VAL="1400" TYPE="uint32" UNITS="MHz" TN="160" TMAX="1200" DMAX="0" SLOPE="zero">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="cpu"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="CPU Speed in terms of MHz"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="CPU Speed"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="pkts_out" VAL="2.73" TYPE="float" UNITS="packets/sec" TN="0" TMAX="300" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="network"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Packets out per second"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Packets Sent"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
<METRIC NAME="swap_free" VAL="0" TYPE="float" UNITS="KB" TN="0" TMAX="180" DMAX="0" SLOPE="both">
<EXTRA_DATA>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="GROUP" VAL="memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="DESC" VAL="Amount of available swap memory"/>
<EXTRA_ELEMENT NAME="TITLE" VAL="Free Swap Space"/>
</EXTRA_DATA>
</METRIC>
</HOST>
</CLUSTER>
</GANGLIA_XML>
Connection closed by foreign host.
где 8649 стандартный порт Ganglia.
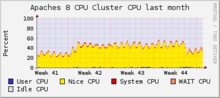
Загрузка серверов
Викимедиа, октябрь 2010 года

Отказ европейских серверов
Викимедиа, второе сентября 2010 года
gmetad
gmetad (Ganglia метадемон) Для сбора информации и её отображения на стороне пользователя в системе Ganglia используется gmetad.[8] По умолчанию для получения данных от других клиентов используется 8651 порт. Конфигурационный файл можно найти в директории:
/etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
Исполняемый файл самого демона находится в директории:
/usr/sbin/gmetad
gmond
gmond (англ. Ganglia monitoring daemon) — демон который запускается на всех узлах для которых необходимо собирать статистику. Конфигурационный файл можно найти в директории:
/etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
Для получения справки о параметрах конфигурационного файла, можно использовать команду:
man gmond.conf
полный вывод команды (англ.)
gmond.conf(5) Ganglia Monitoring System gmond.conf(5)
NAME
gmond.conf - configuration file for ganglia monitoring daemon (gmond)
DESCRIPTION
The gmond.conf file is used to configure the ganglia monitoring daemon (gmond) which is
part of the Ganglia Distributed Monitoring System.
SECTIONS AND ATTRIBUTES
All sections and attributes are case-insensitive. For example, name or NAME or Name or
NaMe are all equivalent.
Some sections can be included in the configuration file multiple times and some sections
are singular. For example, you can have only one cluster section to define the attributes
of the cluster being monitored; however, you can have multiple udp_recv_channel sections
to allow gmond to receive message on multiple UDP channels.
cluster
There should only be one cluster section defined. This section controls how gmond reports
the attributes of the cluster that it is part of.
The cluster section has four attributes: name, owner, latlong and url.
For example,
cluster {
name = "Millennium Cluster"
owner = "UC Berkeley CS Dept."
latlong = "N37.37 W122.23"
url = "http://www.millennium.berkeley.edu/"
}
The name attributes specifies the name of the cluster of machines. The owner tag
specifies the administrators of the cluster. The pair name/owner should be unique to all
clusters in the world.
The latlong attribute is the latitude and longitude GPS coordinates of this cluster on
earth. Specified to 1 mile accuracy with two decimal places per axis in decimal.
The url for more information on the cluster. Intended to give purpose, owner,
administration, and account details for this cluster.
There directives directly control the XML output of gmond. For example, the cluster
configuration example above would translate into the following XML.
<CLUSTER NAME="Millennium Cluster" OWNER="UC Berkeley CS Dept."
LATLONG="N37.37 W122.23" URL="http://www.millennium.berkeley.edu/">
...
</CLUSTER>
host
The host section provides information about the host running this instance of gmond.
Currently only the location string attribute is supported. Example:
host {
location = "1,2,3"
}
The numbers represent Rack, Rank and Plane respectively.
globals
The globals section controls general characteristics of gmond such as whether is should
daemonize, what user it should run as, whether is should send/receive date and such. The
globals section has the following attributes: daemonize, setuid, user, debug_level, mute,
deaf, allow_extra_data, host_dmax, cleanup_threshold, gexec, send_metadata_interval and
module_dir.
For example,
globals {
daemonize = true
setuid = true
user = nobody
host_dmax = 3600
}
The daemonize attribute is a boolean. When true, gmond will daemonize. When false, gmond
will run in the foreground.
The setuid attribute is a boolean. When true, gmond will set its effective UID to the uid
of the user specified by the user attribute. When false, gmond will not change its
effective user.
The debug_level is an integer value. When set to zero (0), gmond will run normally. A
debug_level greater than zero will result in gmond running in the foreground and
outputting debugging information. The higher the debug_level the more verbose the output.
The mute attribute is a boolean. When true, gmond will not send data regardless of any
other configuration directives.
The deaf attribute is a boolean. When true, gmond will not receive data regardless of any
other configuration directives.
The allow_extra_data attribute is a boolean. When false, gmond will not send out the
EXTRA_ELEMENT and EXTRA_DATA parts of the XML. This might be useful if you are using your
own frontend to the metric data and will like to save some bandwith.
The host_dmax value is an integer with units in seconds. When set to zero (0), gmond will
never delete a host from its list even when a remote host has stopped reporting. If
host_dmax is set to a positive number then gmond will flush a host after it has not heard
from it for host_dmax seconds. By the way, dmax means "delete max".
The cleanup_threshold is the minimum amount of time before gmond will cleanup any hosts or
metrics where tn > dmax a.k.a. expired data.
The gexec boolean allows you to specify whether gmond will announce the hosts availability
to run gexec jobs. Note: this requires that gexecd is running on the host and the proper
keys have been installed.
The send_metadata_interval establishes an interval in which gmond will send or resend the
metadata packets that describe each enabled metric. This directive by default is set to 0
which means that gmond will only send the metadata packets at startup and upon request
from other gmond nodes running remotely. If a new machine running gmond is added to a
cluster, it needs to announce itself and inform all other nodes of the metrics that it
currently supports. In multicast mode, this isn't a problem because any node can request
the metadata of all other nodes in the cluster. However in unicast mode, a resend
interval must be established. The interval value is the minimum number of seconds between
resends.
The module_dir is an optional parameter indicating the directory where the DSO modules are
to be located. If absent, the value to use is set at configure time with the
--with-moduledir option which will default if omitted to the a subdirectory named
"ganglia" in the directory where libganglia will be installed.
For example, in a 32-bit Intel compatible Linux host that is usually:
/usr/lib/ganglia
udp_send_channel
You can define as many udp_send_channel sections as you like within the limitations of
memory and file descriptors. If gmond is configured as mute this section will be ignored.
The udp_send_channel has a total of seven attributes: mcast_join, mcast_if, host, port,
ttl, bind and bind_hostname. bind and bind_hostname are mutually exclusive.
For example, the 2.5.x version gmond would send on the following single channel by
default...
udp_send_channel {
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
}
The mcast_join and mcast_if attributes are optional. When specified gmond will create the
UDP socket and join the mcast_join multicast group and send data out the interface
specified by mcast_if.
You can use the bind attribute to bind to a particular local address to be used as the
source for the multicast packets sent or let gmond resolve the default hostname if
bind_hostname = yes.
If only a host and port are specified then gmond will send unicast UDP messages to the
hosts specified.
You could specify multiple unicast hosts for redundancy as gmond will send UDP messages to
all UDP channels.
Be carefull though not to mix multicast and unicast attributes in the same
udp_send_channel definition.
For example...
udp_send_channel {
host = host.foo.com
port = 2389
}
udp_send_channel {
host = 192.168.3.4
port = 2344
}
would configure gmond to send messages to two hosts. The host specification can be an
IPv4/IPv6 address or a resolvable hostname.
udp_recv_channel
You can specify as many udp_recv_channel sections as you like within the limits of memory
and file descriptors. If gmond is configured deaf this attribute will be ignored.
The udp_recv_channel section has following attributes: mcast_join, bind, port, mcast_if,
family. The udp_recv_channel can also have an acl definition (see ACCESS CONTROL LISTS
below).
For example, the 2.5.x gmond ran with a single udp receive channel...
udp_recv_channel {
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
bind = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
}
The mcast_join and mcast_if should only be used if you want to have this UDP channel
receive multicast packets the multicast group mcast_join on interface mcast_if. If you do
not specify multicast attributes then gmond will simply create a UDP server on the
specified port.
You can use the bind attribute to bind to a particular local address.
The family address is set to inet4 by default. If you want to bind the port to an inet6
port, you need to specify that in the family attribute. Ganglia will not allow IPV6=>IPV4
mapping (for portability and security reasons). If you want to listen on both inet4 and
inet6 for a particular port, explicitly state it with the following:
udp_recv_channel {
port = 8666
family = inet4
}
udp_recv_channel {
port = 8666
family = inet6
}
If you specify a bind address, the family of that address takes precedence. f your IPv6
stack doesn't support IPV6_V6ONLY, a warning will be issued but gmond will continue
working (this should rarely happen).
Multicast Note: for multicast, specifying a bind address with the same value used for
mcast_join will prevent unicast UDP messages to the same port from being processed.
tcp_accept_channel
You can specify as many tcp_accept_channel sections as you like within the limitations of
memory and file descriptors. If gmond is configured to be mute, then these sections are
ignored.
The tcp_accept_channel has the following attributes: bind, port, interface, family and
timeout. A tcp_accept_channel may also have an acl section specified (see ACCESS CONTROL
LISTS below).
For example, 2.5.x gmond would accept connections on a single TCP channel.
tcp_accept_channel {
port = 8649
}
The bind address is optional and allows you to specify which local address gmond will bind
to for this channel.
The port is an integer than specifies which port to answer requests for data.
The family address is set to inet4 by default. If you want to bind the port to an inet6
port, you need to specify that in the family attribute. Ganglia will not allow IPV6=>IPV4
mapping (for portability and security reasons). If you want to listen on both inet4 and
inet6 for a particular port, explicitly state it with the following:
tcp_accept_channel {
port = 8666
family = inet4
}
tcp_accept_channel {
port = 8666
family = inet6
}
If you specify a bind address, the family of that address takes precedence. If your IPv6
stack doesn't support IPV6_V6ONLY, a warning will be issued but gmond will continue
working (this should rarely happen).
The timeout attribute allows you to specify how many microseconds to block before closing
a connection to a client. The default is set to 1 second (1000000 usecs). If you have a
very slow connection you may need to increase this value.
The interface is not implemented at this time (use bind).
collection_group
You can specify as many collection_group section as you like within the limitations of
memory. A collection_group has the following attributes: collect_once, collect_every and
time_threshold. A collection_group must also contain one or more metric sections.
The metric section has the following attributes: (one of name or name_match; name_match is
only permitted if pcre support is compiled in), value_threshold and title. For a list of
available metric names, run the following command:
% gmond -m
Here is an example of a collection group for a static metric...
collection_group {
collect_once = yes
time_threshold = 1800
metric {
name = "cpu_num"
title = "Number of CPUs"
}
}
This collection_group entry would cause gmond to collect the cpu_num metric once at
startup (since the number of CPUs will not change between reboots). The metric cpu_num
would be send every 1/2 hour (1800 seconds). The default value for the time_threshold is
3600 seconds if no time_threshold is specified.
The time_threshold is the maximum amount of time that can pass before gmond sends all
metrics specified in the collection_group to all configured udp_send_channels. A metric
may be sent before this time_threshold is met if during collection the value surpasses the
value_threshold (explained below).
Here is an example of a collection group for a volatile metric...
collection_group {
collect_every = 60
time_threshold = 300
metric {
name = "cpu_user"
value_threshold = 5.0
title = "CPU User"
}
metric {
name = "cpu_idle"
value_threshold = 10.0
title = "CPU Idle"
}
}
This collection group would collect the cpu_user and cpu_idle metrics every 60 seconds
(specified in collect_every). If cpu_user varies by 5.0% or cpu_idle varies by 10.0%,
then the entire collection_group is sent. If no value_threshold is triggered within
time_threshold seconds (in this case 300), the entire collection_group is sent.
Each time the metric value is collected the new value is compared with the old value
collected. If the difference between the last value and the current value is greater than
the value_threshold, the entire collection group is send to the udp_send_channels defined.
It's important to note that all metrics in a collection group are sent even when only a
single value_threshold is surpassed.
In addition a user friendly title can be substituted for the metric name by including a
title within the metric section.
By using the name_match parameter instead of name, it is possible to use a single
definition to configure multiple metrics that match a regular expression. The perl
compatible regular expression (pcre) syntax is used. This approach is particularly useful
for a series of metrics that may vary in number between reboots (e.g. metric names that
are generated for each individual NIC or CPU core).
Here is an example of using the name_match directive to enable the multicpu metrics:
metric {
name_match = "multicpu_([a-z]+)([0-9]+)"
value_threshold = 1.0
title = "CPU-\\2 \\1"
}
Note that in the example above, there are two matches: the alphabetical match matches the
variations of the metric name (e.g. idle, system) while the numeric match matches the CPU
core number. The second thing to note is the use of substitutions within the argument to
title.
If both name and name_match are specified, then name is ignored.
Modules
A modules section contains the parameters that are necessary to load a metric module. A
metric module is a dynamically loadable module that extends the available metrics that
gmond is able to collect. Each modules section contains at least one module section.
Within a module section are the directives name, language, enabled, path and params. The
module name is the name of the module as determined by the module structure if the module
was developed in C/C++. Alternatively, the name can be the name of the source file if the
module has been implemented in a interpreted language such as python. A language
designation must be specified as a string value for each module. The language directive
must correspond to the source code language in which the module was implemented (ex.
language = "python"). If a language directive does not exist for the module, the assumed
language will be "C/C++". The enabled directive allows a metric module to be easily
enabled or disabled through the configuration file. If the enabled directive is not
included in the module configuration, the enabled state will default to "yes". One thing
to note is that if a module has been disabled yet the metric which that module implements
is still listed as part of a collection group, gmond will produce a warning message.
However gmond will continue to function normally by simply ignoring the metric. The path
is the path from which gmond is expected to load the module (C/C++ compiled dynamically
loadable module only). The params directive can be used to pass a single string parameter
directly to the module initialization function (C/C++ module only). Multiple parameters
can be passed to the module's initialization function by including one or more param
sections. Each param section must be named and contain a value directive. Once a module
has been loaded, the additional metrics can be discovered by invoking gmond -m.
modules {
module {
name = "example_module"
enabled = yes
path = "modexample.so"
params = "An extra raw parameter"
param RandomMax {
value = 75
}
param ConstantValue {
value = 25
}
}
}
Include
This directive allows the user to include additional configuration files rather than
having to add all gmond configuration directives to the gmond.conf file. The following
example includes any file with the extension of .conf contained in the directory conf.d as
if the contents of the included configuration files were part of the original gmond.conf
file. This allows the user to modularize their configuration file. One usage example
might be to load individual metric modules by including module specific .conf files.
include ('/etc/ganglia/conf.d/*.conf')
ACCESS CONTROL
The udp_recv_channel and tcp_accept_channel directives can contain an Access Control List
(ACL). This ACL allows you to specify exactly which hosts gmond process data from.
An example of an acl entry looks like
acl {
default = "deny"
access {
ip = 192.168.0.4
mask = 32
action = "allow"
}
}
This ACL will by default reject all traffic that is not specifically from host 192.168.0.4
(the mask size for an IPv4 address is 32, the mask size for an IPv6 address is 128 to
represent a single host).
Here is another example
acl {
default = "allow"
access {
ip = 192.168.0.0
mask = 24
action = "deny"
}
access {
ip = ::ff:1.2.3.0
mask = 120
action = "deny"
}
}
This ACL will by default allow all traffic unless it comes from the two subnets specified
with action = "deny".
EXAMPLE
The default behavior for a 2.5.x gmond would be specified as...
udp_recv_channel {
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
bind = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
}
udp_send_channel {
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
}
tcp_accept_channel {
port = 8649
}
To see the complete default configuration for gmond simply run:
% gmond -t
gmond will print out its default behavior in a configuration file and then exit.
Capturing this output to a file can serve as a useful starting point for creating your own
custom configuration.
% gmond -t > custom.conf
edit custom.conf to taste and then
% gmond -c ./custom.conf
NOTES
The ganglia web site is at http://ganglia.info/.
COPYRIGHT
Copyright (c) 2005 The University of California, Berkeley
ganglia/3.1.7 2010-02-17 gmond.conf(5)
Исполняемый файл находится в директории:
/usr/sbin/gmond
Модули
gstat
gstat (англ. Ganglia Cluster Status Tool) — утилита командной строки, позволяющая импортировать информацию из Ganglia в другие приложения.[9]
/usr/bin/gstat
Для того чтобы отобразить список основных команд, используется команда:
Для отображение полной справочной информации можно воспользоваться командой man:
gmetric
Используется для ввода данных из сторонних источников в Ganglia.[10]
/usr/bin/gmetric
gexec
gexec (gexecd) — это масштабируемая система удаленного выполнения задач (программ) в кластерах, которая может работать совместно с системой Ganglia. Для удаленного выполнения параллельных (распределенных) заданий используется RSA аутентификация (демон authd).[11] Система прозрачно перенаправляет программные потоки (stdin, stdout, stderr) и события между распределенными процессами, что позволяет создавать распределенную среду переменных окружения и масштабировать систему до более чем 1000 узлов в составе, без потери надежности. Механизм работы основывается на создании древовидного массива всех TCP сокетов между узлами и распространении управляющей информации по всему дереву. С помощью иерархической системы управления, gexec распределяет как и вычислительные задания, так и ресурсы. Это позволяет устранить проблемы, связанные с ограничениями каждого из узлов, например, ограничение на количество открытых дескрипторов файлов.[12]
Для получения списка хостов в кластере gexec опрашивает узел на котором установлен модуль gmond:
# export LD_ASSUME_KERNEL="2.2.5"
# export GEXEC_GMOND_SVRS="host1 host2"
# gexec -n 0 hostname
1 host1
4 host4
3 host3
0 host0
2 host2
Если узлы на которых запущен gmond недоступны, то список входящих в кластер узлов берется из переменой окружения GEXEC_SVRS.
В gexec интегрирована возможность распределения нагрузки в кластере. Информация о степени загружености узлов запрашивается у gmond. Для балансировки нагрузки задание запускается на наименее загруженных узлах:
gexec -n 5 program
т.е. вышеописанная команда запустит на исполнение программу program на пяти наименее загруженных узлах кластера.[9]
Для включения поддержки gexec в Ganglia необходимо установить соответствующую переменную в конфигурационном файле gmond.conf:
globals{
•••
gexec = yes
•••
}
этот параметр означает, что каждая машина на которой запущен демон gmond будет рассылать специальное сообщение о том, что на машине установлена gexec.
Если вы компилируете Ganglia из исходных кодов, то необходимо явно включить поддержку gexec на стадии конфигурирования:
% ./configure—enable-gexec
gexec можно использовать для выполнения параллельных задач:[13]
gexec -n 12 parprog -in indata.${GEXEC_MY_VNN} -out outdata.${GEXEC_MY_VNN}
каждая из программ parprog получит свою часть данных и сформирует свой результат.
RRDtool
Хранение и визуализация данных (графики) осуществляется в Ganglia с помощью инструментария RRDtool.
См. также
Примечания
Литература
Ссылки
 График системы Ganglia, отображающий количество правок статей в Википедии. Отчетливо виден интервал когда сервер Викимедиа перестал отвечать.
График системы Ganglia, отображающий количество правок статей в Википедии. Отчетливо виден интервал когда сервер Викимедиа перестал отвечать.
 Загрузка серверов Викимедиа, октябрь 2010 года
Загрузка серверов Викимедиа, октябрь 2010 года
 Отказ европейских серверов Викимедиа, второе сентября 2010 года
Отказ европейских серверов Викимедиа, второе сентября 2010 года

